
Global Trade Item Number (GTIN)

What is a Global Trade Item Number (GTIN)?
A Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) is a standardized product identification system that helps businesses distinguish products in the global marketplace. This universal product ID enables accurate identification of trade items, products, and services throughout the supply chain. GTINs are part of the GS1 GTIN family of standardized global data structures, serving as the foundation for efficient supply chain management and international trade.
GTINs function as a universal product language, allowing businesses to identify items consistently across international borders. Each trade item is assigned its own GTIN to differentiate it from other goods, preventing mix-ups between similar products. The unique nature of GTINs makes them invaluable tools for sharing product information between trade partners and managing inventory in the supply chain.
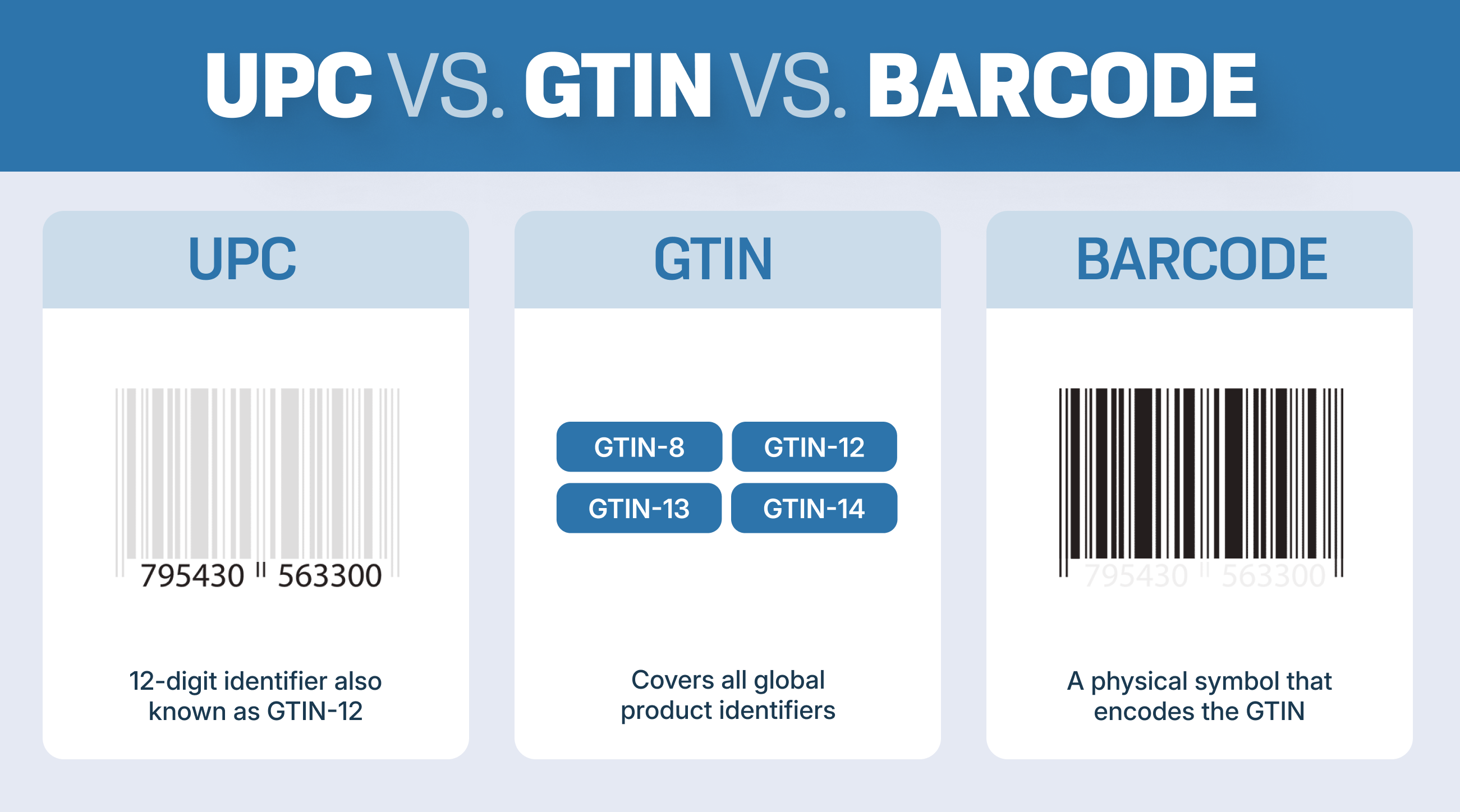
The GTIN system encompasses four different structures:
- GTIN-8: An 8-digit number used outside North America for small retail items
- GTIN-12: A 12-digit number commonly used in North America, synonymous with UPC (Universal Product Code)
- GTIN-13: A 13-digit number used outside North America, equivalent to the EAN barcode (European Article Number)
- GTIN-14: A 14-digit number that identifies trade item groupings like cases or set packs
While GTINs are often associated with barcodes, they actually represent the data encoded within various carriers. Most consumers encounter GTINs as the digits beneath product barcodes. These standardized identifiers can also be found in radio frequency identification (RFID) tags and QR codes.
Modern commerce relies on GTINs in two primary ways. First, they work through barcodes that are scanned at points of sale, care, or distribution centers to capture accurate data. Second, in e-commerce, GTINs ensure customers receive exactly what they ordered. They also serve as keys to access product information such as prices, attributes, and other data shared between trading partners.
GTINs do more than just identify products. These numbers create a standardized way to identify items, which helps prevent errors and optimizes processes throughout logistics and distribution networks. GTINs also enable automated data capture, improving inventory management and ensuring product accuracy for customers.
Bar Codes Talk provides legitimate GTINs with a "works for Amazon guarantee," making them a leading source to purchase GTIN barcodes for your products.
How GTINs Are Used in the Real World
GTINs are the foundation of product identification in the global economy. These standardized identifiers power complex business systems and processes across various industries.
Retail checkout systems
Retail businesses depend on GTINs in barcodes to run their point-of-sale operations smoothly. When a cashier scans a product, the GTIN connects to the store's database, instantly retrieving the price and updating inventory levels. This standardized system accelerates checkout times through accurate product identification and maintains precise stock records. The GTIN acts as the key to unlock product details like prices and categories, streamlining the entire checkout process.
Online marketplaces
E-commerce platforms heavily rely on GTIN numbers for product listing and identification. For instance, Amazon requires GTINs for 25 different product categories to ensure quality and authenticity. Products in these categories must have properly registered GTINs before listing. Bar Codes Talk sells legitimate GTINs that come with a "works for Amazon guarantee," making them a trusted source for GTIN barcodes. These universal identifiers help boost product visibility on search engines and marketplaces, enabling customers to find items more easily and improving order fulfillment processes.
Warehouse and logistics
Supply chain operations use GTINs to control and track inventory, ensuring products remain correctly identified throughout their journey. These unique codes facilitate automated inventory tracking as goods move through the system. Teams use GTINs to support inventory management strategies like "first in, first out" (FIFO), which maintains product quality and prevents perishables from spoiling. Without standardized GTINs, suppliers and distributors would need to track goods manually, significantly slowing down operations and reducing supply chain efficiency.
Regulated industries like healthcare
Healthcare organizations rely on GTINs for several critical functions:
- Accurate medication tracking and inventory control
- Prevention of medication errors at points-of-care
- Enhanced patient safety through proper product identification
In healthcare settings, GTINs are linked with batch numbers and expiration dates to track products from production to patient delivery. The healthcare industry adheres to strict regulations regarding GTIN allocation and prohibits GTIN reuse for regulated items. This standard helps protect patients, especially as more healthcare providers implement robotic dispensing systems and barcode verification in their pharmacy operations.
Need valid GTINs/UPCs that pass Amazon verification? Buy barcodes here: https://www.barcodestalk.com/buy-barcodes
Benefits of Using a GTIN Barcode for Your Product
GTINs provide businesses with a significant advantage in today's digital landscape. These unique identifiers transform how companies track, list, and manage products throughout their lifecycle.
Global product recognition
GTINs function as universal product fingerprints, facilitating worldwide item identification. Products with proper GTINs enjoy increased visibility on search platforms and marketplaces. GTIN-matched listings demonstrate a 40% higher click-through rate compared to those without unique identifiers. Google's data reveals that products with GTINs boost sales conversion rates by 20%. These standardized identifiers form the basis of a global product language that connects suppliers, retailers, and consumers, simplifying expansion into international markets.
Fewer listing errors
GTINs significantly reduce product mix-ups throughout the supply chain. Without proper identifiers, products may not appear in searches, could be incorrectly grouped with competitor listings, or have their variants listed inaccurately. The standardized format of GTINs prevents numbering system conflicts and ensures correct product distribution. E-commerce platforms like Google Shopping require accurate GTINs to approve products, categorize them correctly, and optimize their performance.
Better data quality
GTINs directly enhance information accuracy. These unique identifiers maintain consistent product details between supply chain partners, benefiting both internal and external business operations. Marketplaces use accurate GTINs to verify products and link them to rich data from their catalogs, including total reviews, seller ratings, and detailed specifications. This standardization enables price comparison tools to match similar products across different retailers, allowing shoppers to find competitive prices.
Faster inventory management
GTINs revolutionize inventory tracking through automation and standardization. Barcode scanning is significantly faster than manual methods, boosting operational efficiency by 25%. Simple barcode scanning replaces manual data entry and eliminates most stocktaking errors, resulting in fewer inventory checks, immediate product visibility, and faster auditing. GTINs also support specific inventory strategies like FIFO, which is crucial for maintaining product quality, especially for perishable goods.
Bar Codes Talk provides legitimate GTINs with a "works for Amazon guarantee," making them a top choice for purchasing GTIN barcodes for your products.
How to Assign and Manage GTINs
Implementing GTINs effectively requires proper planning and management throughout the product lifecycle. Businesses must follow specific protocols to maintain accurate product identification and ensure retail compliance.
Decide how many GTINs you need
Each unique product requires its own GTIN, including variants by size, color, or packaging configuration. For example, a t-shirt sold in three colors and four sizes will need twelve distinct GTINs. Consider your future growth plans as well—expanding product lines will require additional identifiers.
Buy GTINs from trusted sources like Bar Codes Talk
Bar Codes Talk offers legitimate GTINs with a "works for Amazon guarantee." Unlike many providers that only offer annual licenses, Bar Codes Talk sells barcodes outright—you own them permanently with no renewal fees. Their GTINs originate from GS1-USA before 2002, guaranteeing their uniqueness.
Assign GTINs to each product and variant
Begin by creating a standardized system for product descriptions that simplifies GTIN management. Assign GTINs only to unique combinations of attributes while maintaining consistency across variants. Document these assignments in a central repository for future reference.
Avoid reusing a GTIN Number
As of January 1, 2019, GS1 General Specifications banned GTIN reuse for any sector. A product's GTIN must remain with it indefinitely—even after discontinuation. This rule ensures consistency in digital marketplaces and supports effective product verification.
Keep GTIN records organized
Maintain a centralized database cataloging each GTIN with its corresponding product and key defining attributes. Conduct regular audits to verify accuracy throughout the product's lifecycle. Properly document your organization's processes for creating, assigning, and managing GTINs.
Need valid GTINs/UPCs that pass Amazon verification? Buy barcodes here: https://www.barcodestalk.com/buy-barcodes
Key Takeaways
Understanding GTINs is crucial for modern businesses aiming to streamline operations and expand globally. These unique identifiers serve as universal product fingerprints that enhance efficiency across retail, e-commerce, and supply chain operations.
- GTINs are unique 8-14 digit identifiers that enable consistent global product recognition and prevent misidentification across international markets
- Products with GTINs achieve 40% higher click-through rates and 20% better conversion rates on digital platforms compared to non-GTIN products
- Every product variant (size, color, packaging) requires its own GTIN, and once assigned, GTINs can never be reused for different products
- GTINs automate inventory management, making barcode scanning 10x faster and 25% more efficient than manual tracking methods
- Purchase GTINs from trusted sources like Bar Codes Talk for lifetime ownership with Amazon guarantee, avoiding annual licensing fees
Proper GTIN implementation transforms how businesses manage products globally, reducing errors while improving visibility and operational efficiency across all channels.
FAQs
Q1. What exactly is a Global Trade Item Number (GTIN)? A GTIN is a unique identifier used worldwide to distinguish products in the marketplace. It serves as a universal product language, enabling consistent identification of items across international borders and throughout the supply chain.
Q2. How can I obtain GTINs for my products? You can purchase GTINs from trusted sources like Bar Codes Talk, which offers legitimate GTINs with a "works for Amazon guarantee." These GTINs are sold outright, meaning you own them for life without recurring fees.
Q3. Do I need separate GTINs for product variants? Yes, each unique product variant (such as different sizes, colors, or packaging configurations) requires its own GTIN. For example, if you sell a t-shirt in three colors and four sizes, you'll need twelve distinct GTINs.
Q4. What are the benefits of using GTINs for my products? Using GTINs provides global product recognition, reduces listing errors, improves data quality, and enables faster inventory management. Products with GTINs have been shown to achieve higher click-through rates and better conversion rates on digital platforms.
Q5. Can I reuse a GTIN after discontinuing a product? No, GTINs should never be reused, even after a product is discontinued. This rule, established in 2019, ensures consistency in digital marketplaces and prevents confusion in product identification.
